870 Economic Carbon Granular (ECG)
- Manufactured using 100% pure virgin coconut shell activated carbon
- All parts are sealed using advanced friction welding, eliminating the need for adhesives
- Thermoplastic top mounted gasket eliminating risk of dioxin release and bacterial growth associated with natural rubber.
- Bacteria-resistant PET pads
- Iodine rating – 1050mg/g
- Suited for chlorine, taste and odour reduction
- Can be used as a standalone water filter or as a pre filter for water purifiers
- Drinking water
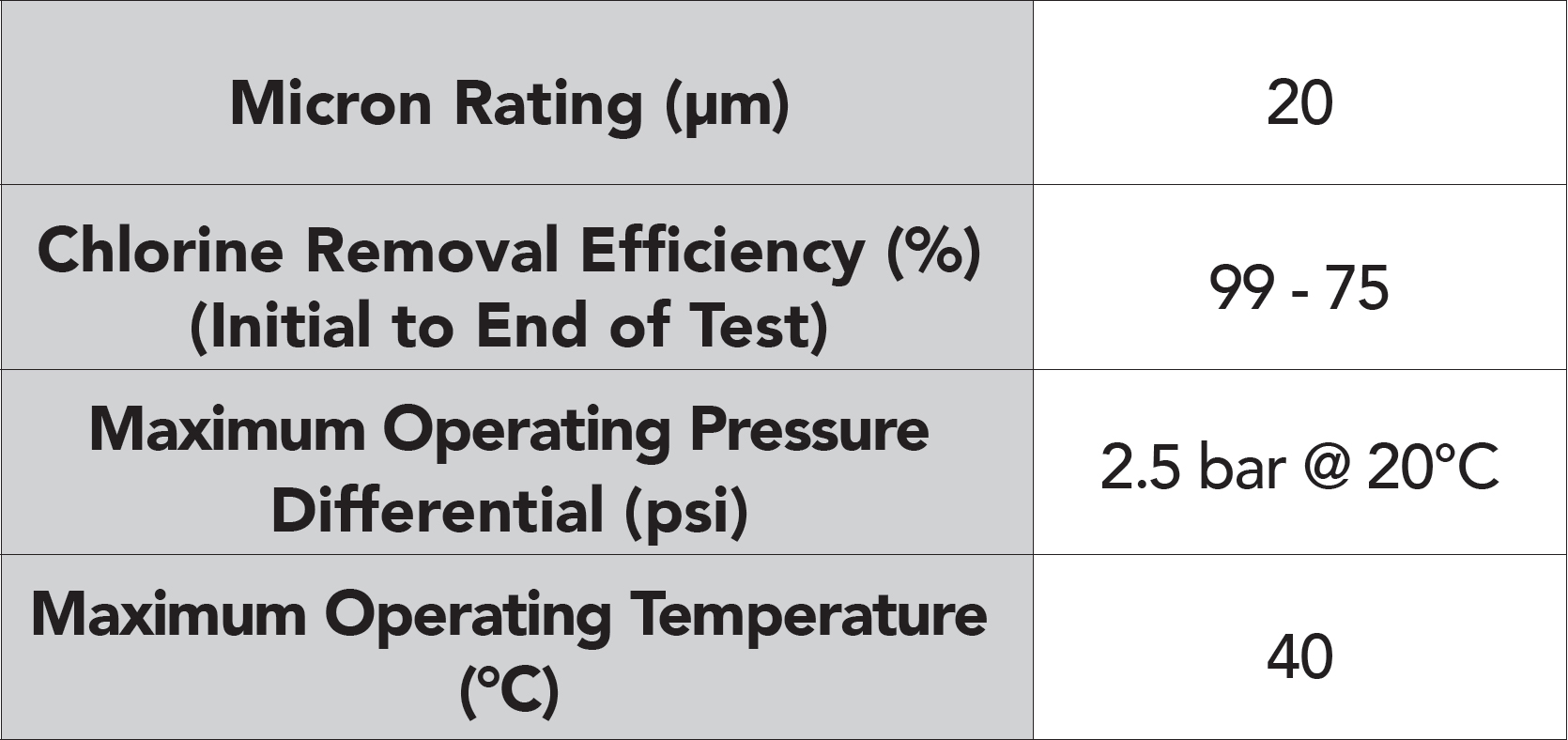

Features & Information
A cost-effective, small scale granular carbon solution for chlorine, taste and odour control.
FAQs - ECG
Refers to the distinctive flavour and smell associated with chlorine in water. Chlorine is commonly used as a disinfectant in water treatment processes to kill bacteria, viruses, and other harmful microorganisms. While chlorine is effective in reducing waterborne pathogens it can leave a residual taste (often described as a bleach-like or chemical flavour) and odour in the treated water.
Removing chlorine from water is often desired for several reason:
- Taste and Odour: chlorine causes an unpleasant taste and odour in water.
- Beverage and Food Quality: natural flavours and characteristics are compromised by the presence of chlorine, specifically yeast.
- Cosmetic and Aesthetics: Chlorine can strip the natural oils from the skin and hair, leading to dryness and potential damage.
- Disinfection Byproducts: Chlorine can react with naturally occurring organic matter in water, forming disinfection byproducts such as trihalomethane and halo-acetic acids. Long-term exposure has been associated with potential health risks, such as cancer.
Removing chlorine from water is often desired for several reasons:
-
- Taste and Odour: chlorine causes an unpleasant taste and odour in water.
- Beverage and Food Quality: natural flavours and characteristics are compromised by the presence of chlorine, specifically yeast.
- Cosmetic and Aesthetics: Chlorine can strip the natural oils from the skin and hair, leading to dryness and potential damage.
- Disinfection Byproducts: Chlorine can react with naturally occurring organic matter in water, forming disinfection byproducts such as trihalomethane and halo-acetic acids. Long-term exposure has been associated with potential health risks, such as cancer.
Carbon filters work by utilising activated carbon, a highly porous material with a large surface area. When water passes through the carbon filter, contaminants come into contact with the activated carbon. The contaminants are either adsorbed onto the carbon’s surface or undergo chemical reactions that neutralise them. This process effectively removes impurities such as chlorine, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), odours, and some heavy metals, resulting in cleaner and purer water.


